Phytochemical and antioxidant screening of the fruit and seed extract of phoenix dactylifera linn and evaluation of its toxicological profile in albino rats
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: Phoenix dactylifera (date palm) is a common plant with various known benefits. The plant's health benefits have been associated with its high antioxidant profite.
Objectives: To conduct phytochemical, antioxidant, metal and vitamin analysis, and evaluate the hematological and biochemical effects of the fruit and seed extracts of Phoenix dactylifera.
Methods: Evaluation of Phoenix dactylifera for phytochemicals was conducted using standard methods. Quantitative determination of total phenolics, total flavonoids, and various in vitro antioxidant activities (DPPH and FRAP) was carried out using colorimetric methods.
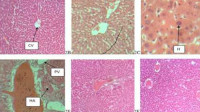
Results: Phytochemical analysis shows the presence of alkaloids, flavonoids, terpenoids, phenols and tannins in both extracts. The antioxidant activity was also found to be 83.86 to 88.43% for seeds and 63.49 to 85.06% for fruit. The fruit and seed extracts contained Vit A (0.52/0.46 1U/100g), C (16.26/0.79 mg/100g), and E(45.63/49.87 mg/100g). Metal analysis indicated the presence of Mg, Zn, Ca, Cu, and K with the seeds having a higher concentration of the metals than the fruits. Serum biochemical analysis indicated no deleterious effects on vital organs, no significant changes observed in the levels of ALT, AST, albumin, bilirubin and total protein. The histopathological findings in the kidney and liver of fats treated with the extract were found to be normal. Hematological parameters showed no significant difference from control but MPV and MCV concentration were decreased significantiy (p<0.05) in animals
treated with 100 mg/kg of the methanol seed extract. The body weights increased in a dose-dependent manner in rats treated with fruits extract. Conversely, a decrease in body weight was observed in those treated with seeds extract.
Conclusion: The seed and fruit extract of Phoenix dactylifera did not produce any toxic effect in the rats.
Downloads
Article Details
Issue
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.